Updated on December 11, 2025, by OpenEDR
Cyber threats are rising across every industry, and businesses can no longer afford weak endpoint protection. Fortunately, Microsoft provides a robust, built-in defense tool for Windows devices: Windows Defender Security Center. But what exactly does it do, how reliable is it, and how can IT teams get the most value from it?
In this detailed guide, we break down Windows Defender Security Center—what it is, how it works, the features it provides, and why it’s an essential component of any organization’s cybersecurity strategy. Whether you’re securing endpoints for a small business or managing thousands of devices across an enterprise, understanding this tool can significantly strengthen your security posture.
What Is Windows Defender Security Center? (Simple Definition)
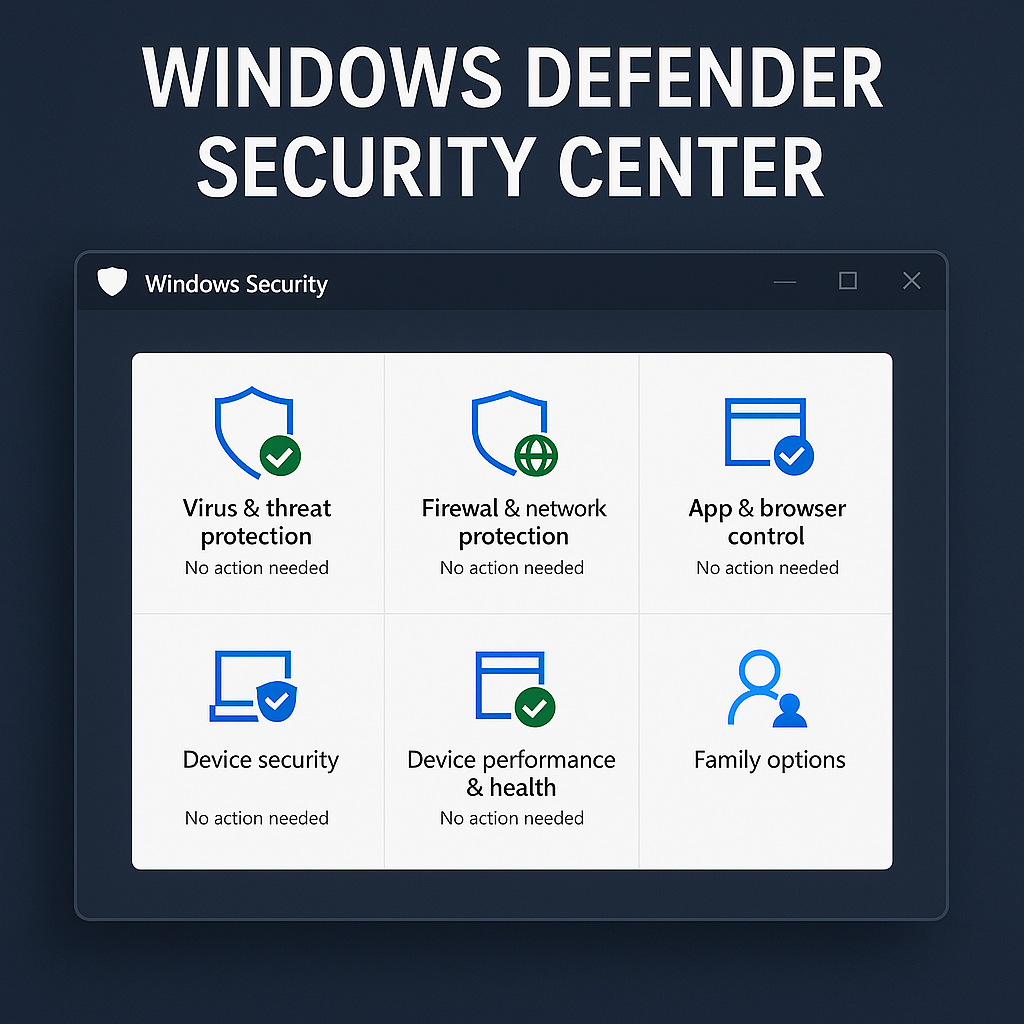
Windows Defender Security Center is Microsoft’s built-in dashboard that centralizes all Windows security settings, tools, and threat-monitoring capabilities under one unified interface. It allows users and IT administrators to monitor antivirus protection, firewall configurations, device performance, app security, and overall system health.
The Windows Defender Security Center is included by default in Windows 10 and Windows 11, offering strong protection without requiring third-party software.
Why Windows Defender Security Center Matters for Businesses
Before diving into features and benefits, it’s essential to understand why Windows Defender matters in today’s cybersecurity landscape.
1. Cyberattacks Are More Sophisticated Than Ever
Attackers use:
Ransomware
Zero-day exploits
Fileless malware
Credential theft
Phishing kits
Windows Defender helps protect against these threats with real-time monitoring and cloud-based intelligence.
2. Windows Devices Dominate the Business Market
With more than 70% of enterprise endpoints running Windows, Defender plays a critical security role.
3. Built-In Security Reduces Costs
Organizations can avoid expensive third-party antivirus solutions.
4. Defender Integrates with Microsoft Cloud Services
Tools like Microsoft Intune, Azure AD, and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint strengthen device security.
5. Compliance Requirements
Windows Defender supports standards such as:
HIPAA
GDPR
PCI-DSS
CMMC
Organizations can implement Defender as part of a compliant security framework.
Key Features of Windows Defender Security Center
Let’s dive into the core features that make Windows Defender Security Center powerful for endpoint security.
1. Virus & Threat Protection
This is the heart of Windows Defender antivirus.
Key features include:
Real-time protection
Cloud-powered threat detection
Automatic scanning
Ransomware protection
Controlled folder access
Microsoft’s cloud-based intelligence analyzes billions of signals, enabling Defender to detect emerging threats quickly.
2. Firewall & Network Protection
Windows Defender provides a built-in firewall that monitors incoming and outgoing traffic.
Capabilities include:
Network threat blocking
Application firewall rules
Domain, private, and public network profiles
Protection against remote exploits
IT teams can configure firewall rules centrally using Group Policy or Intune.
3. App & Browser Control
This section helps protect users from unsafe apps, websites, and downloads.
Features include:
SmartScreen reputation filtering
Exploit protection
Application reputation-based blocking
Web threat prevention
SmartScreen blocks malicious websites and phishing attempts across Microsoft Edge and Windows apps.
4. Device Security
Windows leverages hardware-based security for deeper endpoint protection.
Includes:
Core isolation
Secure Boot
TPM (Trusted Platform Module)
Hardware security-based isolation
These features protect against firmware attacks and rootkits.
5. Device Performance & Health
This section monitors:
Battery life
Storage capacity
Windows updates
Startup performance
Businesses benefit from improved device uptime and reliability.
6. Family Options (For Home Users)
While less relevant for business, these controls offer parental protection and monitoring.
7. Integration With Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
For enterprises, this integration unlocks:
Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR)
Threat analytics
Attack surface reduction
Automated investigation and remediation
This is critical for Zero Trust and SOC operations.
How Windows Defender Security Center Protects Against Modern Threats
Windows Defender has evolved far beyond basic antivirus capabilities. It now uses advanced security technologies.
1. Cloud-Delivered Protection
Microsoft’s security cloud evaluates billions of new signals daily, providing real-time detection.
2. Behavior-Based Malware Detection
Instead of relying only on signatures, Defender identifies suspicious behavior.
Examples:
Unexpected script execution
Unusual PowerShell commands
Unauthorized privilege escalation
3. Sandboxing
Defender runs certain components in isolated environments, reducing risk.
4. Machine Learning Classification
AI-driven threat models detect new malware families quickly.
5. Ransomware Protection
Windows Defender includes:
Controlled folder access
Rollback capabilities (Windows 10/11 integrated with OneDrive)
Benefits of Using Windows Defender Security Center
1. Free and Built-In
No additional licensing required.
2. Enterprise-Grade Protection
Especially when combined with Defender for Endpoint.
3. Low System Impact
Runs efficiently without slowing down devices.
4. Automatic Updates
Defender receives daily and even hourly updates through the cloud.
5. Strong Integration With Windows OS
Better compatibility and fewer conflicts than third-party security tools.
Limitations of Windows Defender Security Center
While powerful, it has some limitations organizations should consider.
1. Basic EDR Capabilities on Its Own
Full EDR requires Microsoft Defender for Endpoint licensing.
2. Limited Cross-Platform Support
Microsoft now supports macOS, iOS, Android, and Linux through paid plans, but the free version is Windows-only.
3. Default Settings May Not Be Enough
IT teams must customize policies for optimal protection.
4. Attackers Know It Well
As a widely used tool, attackers often study how to bypass it.
How to Access Windows Defender Security Center
You can access the dashboard through:
Start Menu → Windows Security
Or search:
“Windows Defender Security Center” or “Windows Security”
How to Configure Essential Settings
To maximize protection:
1. Turn On Real-Time Protection
Prevents immediate execution of malware.
2. Enable Cloud Protection
Improves detection of emerging threats.
3. Use Tamper Protection
Prevents unauthorized changes to security settings—even by admin users.
4. Turn On Controlled Folder Access
Blocks ransomware from modifying critical files.
5. Enable SmartScreen
Protects users from malicious websites and downloads.
6. Configure Firewall Rules
Restrict unnecessary inbound and outbound connections.
Windows Defender Security Center vs Third-Party Antivirus
| Feature | Windows Defender | Third-Party Antivirus |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Free | Paid |
| Cloud Protection | Strong | Varies |
| EDR | Requires add-on | Often included |
| System Impact | Low | Medium |
| OS Integration | Excellent | Limited |
| Cross-Platform | Limited free | Stronger support |
Many organizations pair Windows Defender with advanced endpoint tools like Xcitium OpenEDR® for stronger visibility and containment.
Best Practices for Using Windows Defender Security Center
To strengthen your security posture:
1. Combine Defender With EDR Tools
Enhanced threat detection protects against unknown attacks.
2. Apply Zero Trust Principles
Identity-based access reduces lateral movement.
3. Segment Your Network
Limit blast radius if malware spreads.
4. Use Strong Authentication
Protect Windows accounts with MFA and passwordless solutions.
5. Monitor Alerts Daily
Set up alert forwarding to SIEM tools for security teams.
6. Train Employees
Teach users how to detect phishing and malware scams.
7. Update Systems Frequently
Patching reduces vulnerabilities attackers exploit.
Future Improvements Expected for Windows Defender
Microsoft will continue to expand capabilities such as:
AI-driven threat prevention
Unified cloud security dashboards
Network threat analytics
Offline behavioral analysis
Hardware-based virtualization improvements
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is Windows Defender Security Center?
A built-in dashboard that centralizes antivirus, firewall, app protection, and device security controls on Windows.
2. Is Windows Defender enough for business use?
It’s strong, but pairing it with EDR or a managed security solution provides better protection.
3. Is Windows Defender free?
Yes, all built-in features are free with Windows 10 and 11.
4. Does Windows Defender slow down computers?
No, it is optimized for low resource usage.
5. How often does Defender update?
It updates automatically multiple times per day.
Final Thoughts
Windows Defender Security Center provides powerful, built-in protection for Windows users and businesses. Its combination of antivirus, firewall, SmartScreen protection, ransomware defenses, and hardware-based security makes it one of the strongest default security platforms available today.
However, as threats grow more advanced, organizations benefit from pairing Defender with more comprehensive endpoint protection, threat detection, and Zero Trust strategies.
👉 Ready to strengthen your endpoint security even further?
Start with Xcitium OpenEDR® today:
https://openedr.platform.xcitium.com/register/