Updated on November 19, 2025, by OpenEDR
Have you ever connected to WiFi and wondered whether it’s actually safe? Or why some networks ask for a password while others are open for anyone? Whether at home, in the office, or at a coffee shop, every wireless network uses a specific type of security — and understanding WiFi security types is essential for protecting your personal and business data.
With cyberattacks increasing and WiFi networks becoming targets for hackers, choosing the right WiFi security option is more important than ever. In fact, over 60% of cyberattacks originate from unsecured or weak wireless networks. That means your WiFi security choice isn’t just a checkbox — it’s a crucial layer of protection.
In this friendly, conversational guide, we’ll break down the different WiFi security types, explain how they work, and show you exactly which one you should use in 2025. Whether you’re a cybersecurity professional, IT manager, CEO, or everyday user who wants a safer connection, this guide will help you understand WiFi security clearly.
Let’s dive in.
⭐ What Are WiFi Security Types? (Simple Definition)
WiFi security types are the different authentication and encryption methods used to protect wireless networks from unauthorized access. In simple terms:
👉 They determine who can join your WiFi and how well your data is protected.
These security types encrypt your data so that attackers can’t:
Intercept your information
Read your web traffic
Steal your passwords
Connect to your devices
Break into your home or office network
Different WiFi security types offer different levels of protection. Some are incredibly secure, while others are outdated and dangerous.
⭐ Why WiFi Security Types Matter More Than Ever
Cybercriminals love weak WiFi networks — especially older security types like WEP or unsecured hotspots.
Here’s why choosing the right option matters:
✔ Hackers can steal data through weak WiFi
Passwords, banking info, and personal files can be intercepted.
✔ Business networks are prime targets
Unsecured WiFi gives attackers access to internal systems.
✔ Ransomware attacks often begin with WiFi intrusions
Once inside, malware spreads across the network.
✔ Smart devices and IoT increase risk
Cameras, doorbells, and sensors all connect through WiFi.
✔ Public WiFi is extremely unsafe
Most public networks use outdated security types or no security at all.
Choosing the right WiFi security type reduces your exposure dramatically.
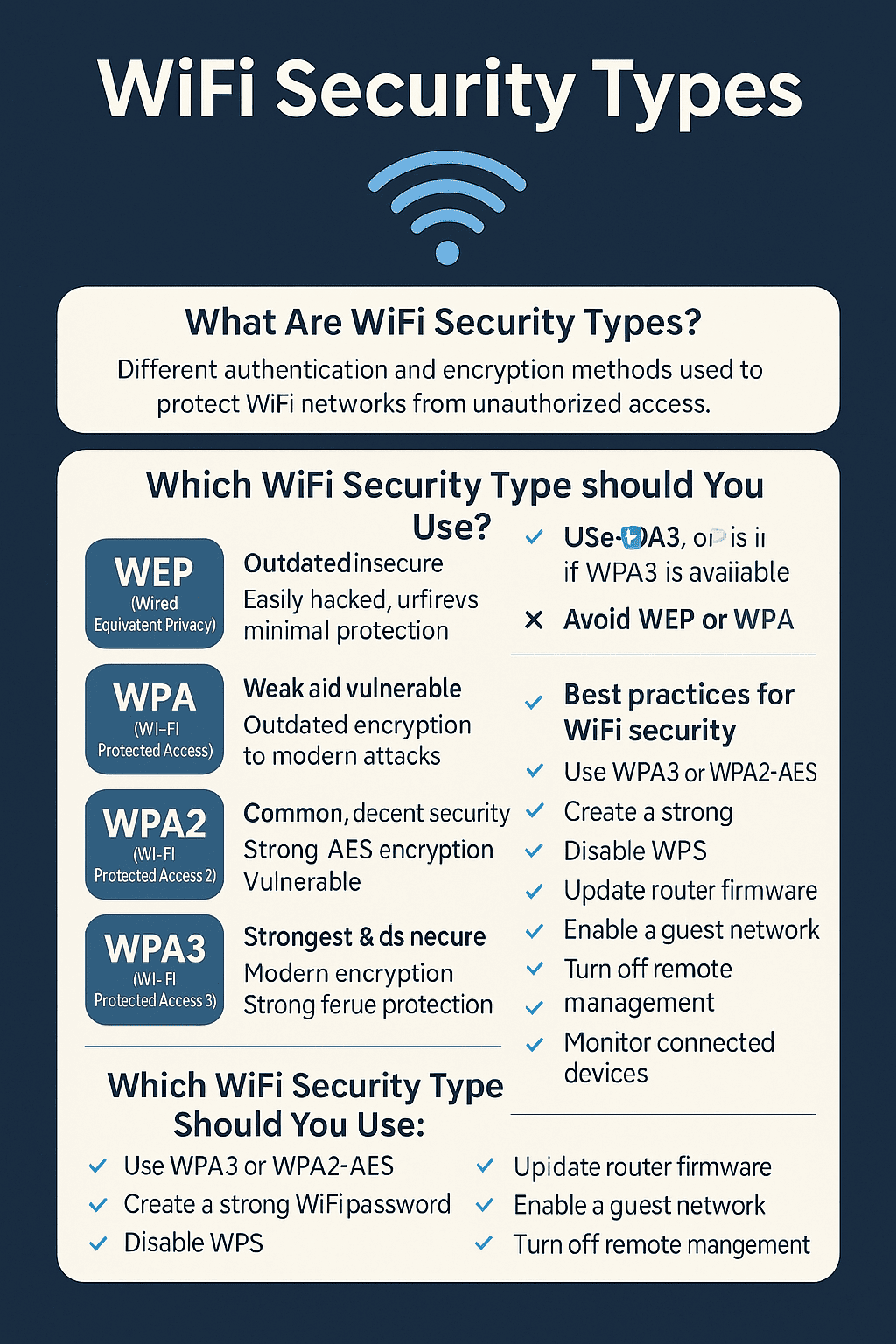
🔐 The 4 Main WiFi Security Types (Explained Simply)
Let’s explore the different types of WiFi security — from weakest to strongest.
1. WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) — OUTDATED & UNSAFE
WEP is the oldest WiFi security type, dating back to the late 1990s.
Why it’s unsafe:
Can be hacked in minutes
Uses weak encryption
Vulnerable to automated cracking tools
Offers almost no real security
Today, WEP should NEVER be used — not at home, not at work, not anywhere.
2. WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) — BETTER, BUT STILL WEAK
WPA replaced WEP but still suffers from major vulnerabilities.
Problems with WPA:
Uses outdated TKIP encryption
Vulnerable to brute-force attacks
Many tools can break WPA networks
Not recommended for modern environments
If your router only has WPA, it’s time to upgrade.
3. WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2) — STILL COMMON, DECENT SECURITY
WPA2 is widely used today and is much stronger than WPA.
Strengths:
Uses advanced AES encryption
Reliable for homes and small offices
Protected from most common attacks
But there’s a catch:
WPA2 is vulnerable to:
KRACK attacks
Key reinstallation vulnerabilities
Password guessing if the key is weak
WPA2 is safe only if you use a strong password.
4. WPA3 — THE STRONGEST & MOST SECURE OPTION (RECOMMENDED)
WPA3 is the latest and best WiFi security type.
Why WPA3 is the strongest:
Uses modern cryptographic standards
Protects against offline password cracking
Secures data even when users choose weak passwords
Offers individualized encryption
Prevents eavesdropping on public WiFi
Stops brute-force attacks
If your router supports WPA3 — use it.
🧩 WPA3 Comes in Two Versions
WPA3-Personal
Best for homes and small offices.
WPA3-Enterprise
Best for companies and organizations; includes:
192-bit encryption
Certificate-based authentication
Strong protection for sensitive data
🔍 Which WiFi Security Type Should You Use?
Here’s the simple answer:
✔ Use WPA3 whenever possible
✔ If unavailable, use WPA2-AES (not TKIP)
✔ Avoid WPA and WEP entirely
In order of strongest → weakest:
WPA3
WPA2-AES
WPA (avoid)
WEP (never use)
🛡️ WiFi Security Modes Explained (PSK vs Enterprise)
Each WiFi security type supports two authentication modes:
1. Personal Mode (WPA2-PSK / WPA3-PSK)
Uses a shared password.
Good for:
Homes
Small offices
Personal networks
Pros:
Easy to set up
Works with most devices
2. Enterprise Mode (WPA2-Enterprise / WPA3-Enterprise)
Uses authentication servers like RADIUS.
Good for:
Corporations
Schools
Healthcare
Government
Large environments
Pros:
Individual logins
Advanced control
Better auditing
Superior security
🛠️ How to Check Your WiFi Security Type (Quick Guide)
You can easily see your current WiFi security type:
On Windows:
Click WiFi icon
Select your network
Click Properties
Scroll to Security Type
On Mac:
Hold Option
Click WiFi icon
Look for Security
On Router Admin Panel:
Type 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1
Login
Go to Wireless Settings
⚠️ Warning: Many Old Routers Don’t Support WPA3
If you can’t find WPA3, your router might be outdated.
It may be time to consider upgrading — especially if:
Your router is older than 5 years
You experience dropped connections
You use many IoT devices
You run a business network
A modern router = better WiFi security + faster performance.
🔥 How Hackers Break Weak WiFi Security
Hackers use various techniques to compromise weak WiFi setups:
✔ Packet sniffing
✔ Deauthentication attacks
✔ Brute-force key guessing
✔ WPA handshake capture
✔ Evil twin attacks (fake WiFi networks)
✔ Man-in-the-middle exploitation
✔ KRACK attacks (on WPA2)
WPA3 blocks almost all of these.
🧠 Best Practices to Improve Your WiFi Security
WiFi security is more than just choosing the right encryption type.
Here’s how to stay protected:
✔ Use WPA3 or WPA2-AES
✔ Create a long, unique WiFi password
✔ Disable WPS (it’s vulnerable)
✔ Change default router password
✔ Update router firmware regularly
✔ Turn off remote management
✔ Use a guest network for visitors
✔ Hide your SSID (optional)
✔ Keep IoT devices on a separate network
✔ Monitor connected devices
Small steps make your network far more secure.
🧭 WiFi Security Types for Businesses & Enterprises
Corporate WiFi requires much stronger controls.
Best options include:
✔ WPA3-Enterprise
✔ RADIUS authentication
✔ Zero Trust Network Access
✔ Network segmentation
✔ EDR on endpoints
✔ VPN for remote access
✔ Continuous monitoring
Business WiFi is often the entry point for major cyberattacks — so securing it is essential.
🎯 Conclusion: WiFi Security Types Matter for Every User
If you’ve been wondering which WiFi security types are safest, here’s the simple answer:
✔ WPA3 is the strongest and best for 2025
✔ WPA2-AES is still safe if WPA3 isn’t available
✔ WPA and WEP should never be used
Choosing the right security type protects your network, devices, and data against modern cyber threats. And with the rise of remote work, smart devices, and highly targeted attacks, strong WiFi security is no longer optional — it’s essential.
🔐 Protect Your Network with Xcitium OpenEDR (Free Registration)
Strengthen your entire cybersecurity posture with powerful endpoint detection and real-time protection.
👉 https://openedr.platform.xcitium.com/register/
❓ FAQs About WiFi Security Types
1. What is the safest WiFi security type?
WPA3 is the strongest and most secure option available today.
2. Is WPA2 still safe?
Yes — as long as it uses AES encryption, not TKIP.
3. Should I disable WPS?
Yes. WPS is vulnerable and easily exploited.
4. Does WiFi password length matter?
Absolutely. Use at least 12–16 characters.
5. Can hackers break into WPA3 networks?
It’s extremely difficult and far less likely compared to WPA2 or older standards.