Updated on December 31, 2025, by OpenEDR
Cyber threats are no longer isolated technical problems—they are business risks with real financial and reputational consequences. Data breaches, ransomware attacks, and supply chain compromises can disrupt operations overnight. This is why cybersecurity risk management has become a top priority for organizations of every size and industry.
Cybersecurity risk management helps businesses identify, assess, and reduce cyber risks before they turn into costly incidents. Instead of reacting to threats after damage occurs, organizations take a proactive, structured approach to managing risk. In this guide, we’ll explain what cybersecurity risk management is, why it matters, and how to implement it effectively across your organization.
What Is Cybersecurity Risk Management?
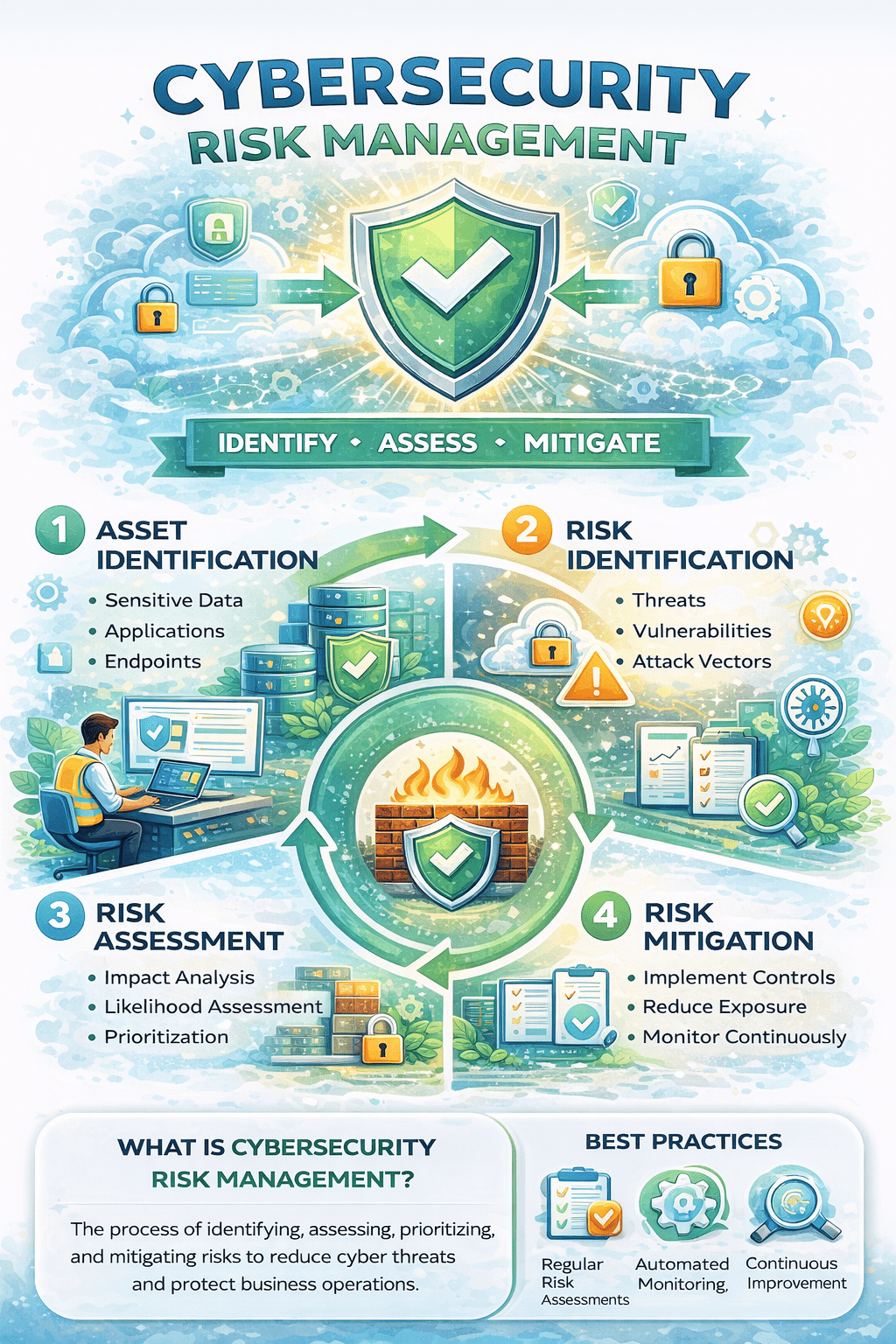
Cybersecurity risk management is the process of identifying, evaluating, prioritizing, and mitigating risks related to cyber threats. It aligns security efforts with business objectives to ensure that risks are reduced to acceptable levels.
Rather than focusing solely on tools or technologies, cybersecurity risk management takes a holistic view. It considers people, processes, technology, and governance to protect critical assets.
At its core, cybersecurity risk management answers three key questions:
What assets are we protecting?
What threats and vulnerabilities exist?
How much risk are we willing to accept?
Why Cybersecurity Risk Management Is Critical Today
Digital transformation has expanded attack surfaces across cloud environments, endpoints, remote workers, and third-party vendors. At the same time, attackers are becoming faster, more organized, and more persistent.
Cybersecurity risk management matters because it:
Reduces the likelihood of breaches
Minimizes business disruption
Supports regulatory compliance
Protects customer trust
Improves decision-making at the executive level
Without a structured risk management approach, security investments often become reactive, fragmented, and inefficient.
Understanding Cyber Risk vs Cyber Threats
Before implementing cybersecurity risk management, it’s important to understand the difference between risks and threats.
Cyber Threats
Threats are potential events or actors that can cause harm, such as:
Malware
Ransomware
Phishing attacks
Insider threats
Cyber Risks
Risk is the likelihood and impact of a threat exploiting a vulnerability.
Cybersecurity risk management focuses on reducing risk—not eliminating all threats, which is impossible.
Core Components of Cybersecurity Risk Management
Effective cybersecurity risk management is built on several foundational components.
1. Asset Identification
You can’t protect what you don’t know exists. The first step is identifying critical assets.
Examples include:
Sensitive data
Applications and systems
Cloud workloads
Endpoints and servers
Intellectual property
Asset classification helps determine where security efforts should be focused.
2. Risk Identification
Once assets are identified, organizations must evaluate potential risks.
This includes:
Identifying vulnerabilities
Assessing threat likelihood
Understanding attack vectors
Common sources of risk include misconfigurations, outdated software, weak credentials, and third-party access.
3. Risk Assessment and Analysis
Cybersecurity risk management requires evaluating how likely a risk is and how severe the impact would be.
Risk assessments typically consider:
Probability of occurrence
Financial impact
Operational disruption
Legal and compliance consequences
Reputational damage
This step helps prioritize risks instead of treating all threats equally.
4. Risk Mitigation and Treatment
After risks are assessed, organizations decide how to handle them.
Common risk treatment options include:
Mitigation: Reduce risk through controls
Avoidance: Eliminate risky activities
Transfer: Shift risk via insurance or contracts
Acceptance: Accept low-level risks
Cybersecurity risk management emphasizes mitigation through preventive and detective controls.
Cybersecurity Risk Management Frameworks
Many organizations use established frameworks to structure their cybersecurity risk management programs.
Popular Frameworks
NIST Cybersecurity Framework
ISO/IEC 27001
COBIT
FAIR (Factor Analysis of Information Risk)
These frameworks provide standardized approaches for identifying, assessing, and managing cyber risk while aligning security with business goals.
Cybersecurity Risk Management Best Practices
Implementing cybersecurity risk management effectively requires consistency and discipline.
Best Practices to Follow
Perform regular risk assessments
Keep asset inventories updated
Prioritize risks based on business impact
Automate risk monitoring where possible
Continuously review and adjust controls
Risk management is not a one-time exercise—it’s an ongoing process.
Role of Leadership in Cybersecurity Risk Management
Cybersecurity risk management is no longer just an IT responsibility. Executive leadership plays a critical role.
Why Leadership Matters
Cyber risk affects revenue and reputation
Strategic decisions influence security posture
Risk tolerance is a business decision
Boards and executives must understand cyber risk in business terms, not just technical metrics.
Cybersecurity Risk Management in Cloud Environments
Cloud adoption introduces new risks that must be addressed.
Cloud-Specific Risk Factors
Shared responsibility models
Misconfigurations
Insecure APIs
Identity and access risks
Cybersecurity risk management in the cloud requires strong visibility, continuous monitoring, and automated controls.
Third-Party and Supply Chain Risk Management
Vendors and partners often have access to sensitive systems.
Key supply chain risks include:
Weak vendor security controls
Excessive third-party permissions
Lack of visibility into vendor environments
Effective cybersecurity risk management includes assessing and monitoring third-party risk regularly.
Cybersecurity Risk Management and Compliance
Compliance requirements often drive cybersecurity investments—but compliance alone is not security.
Cybersecurity risk management helps organizations:
Meet regulatory obligations
Maintain audit readiness
Demonstrate due diligence
Align security controls with compliance frameworks
Common regulations include SOC 2, HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS.
Quantifying Cyber Risk for Better Decisions
Executives often ask: How much risk do we really face?
Modern cybersecurity risk management increasingly uses quantitative approaches to:
Estimate financial impact
Support budget decisions
Compare security investments
Communicate risk to stakeholders
Quantification transforms cybersecurity from a technical issue into a measurable business concern.
Cybersecurity Risk Management and Zero Trust
Zero Trust security aligns naturally with cybersecurity risk management.
Zero Trust principles include:
Never trust by default
Always verify access
Enforce least privilege
Monitor continuously
By assuming breach and limiting access, organizations reduce the potential impact of cyber incidents.
Common Cybersecurity Risk Management Mistakes
Even mature organizations make avoidable mistakes.
Common Pitfalls
Treating risk assessments as annual checklists
Ignoring low-probability, high-impact risks
Over-relying on tools instead of processes
Failing to reassess risks after changes
Poor communication between IT and leadership
Avoiding these mistakes significantly improves risk posture.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Cybersecurity Risk Management
To improve, organizations must measure results.
Key Metrics to Track
Risk reduction over time
Incident frequency and severity
Mean time to detect and respond
Compliance audit results
Control effectiveness
Metrics help demonstrate value and guide continuous improvement.
The Future of Cybersecurity Risk Management
Cybersecurity risk management continues to evolve alongside threats and technology.
Emerging Trends
AI-driven risk analysis
Continuous risk assessment
Automated remediation
Integrated security platforms
Business-aligned risk reporting
Organizations that modernize their approach will be better prepared for future threats.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is cybersecurity risk management?
Cybersecurity risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and reducing cyber risks to acceptable levels.
2. Why is cybersecurity risk management important?
It helps prevent breaches, reduce business disruption, and align security investments with business priorities.
3. Who is responsible for cybersecurity risk management?
Responsibility is shared between IT, security teams, leadership, and the board.
4. How often should cyber risk assessments be done?
Risk assessments should be conducted regularly and whenever significant changes occur.
5. Is cybersecurity risk management required for compliance?
While not always mandated, it strongly supports compliance with regulations and standards.
Final Thoughts: Turning Cyber Risk into Business Resilience
Cyber threats are inevitable—but unmanaged risk is not. Cybersecurity risk management provides organizations with a structured, proactive way to reduce exposure, protect critical assets, and support long-term business resilience.
For IT leaders and executives alike, managing cyber risk is no longer optional. It’s a strategic necessity that directly impacts growth, trust, and survival.
Take Control of Cyber Risk Today
Effective cybersecurity risk management requires visibility, control, and real-time threat prevention. If you’re ready to strengthen your security posture and reduce risk across your environment:
👉 Start protecting your organization with Xcitium’s OpenEDR
Register Now